Scientists from IBM Security have recently made a startlingly simple discovery regarding a method to hijack and manipulate live conversations through the use of artificial intelligence (AI).

The “audio-jacking” attack utilizes deepfake audio technology and generative AI, incorporating OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Meta’s Llama-2.
Audio Jacking
Researchers programmed the AI to analyze audio from two sources during a live communication, such as a phone conversation, as part of the experiment.
Upon hearing a particular keyword or phrase, the AI is further directed to intercept and manipulate the associated audio before transmitting it to the intended recipient.
As stated in an IBM Security blog post, the experiment concluded with the AI effectively intercepting the audio of a speaker whom another human speaker requested to provide their bank account information.
The AI then generated a different account number, substituting deepfake audio for the genuine voice. The occurrence went unnoticed by the “victims” involved in the experiment.
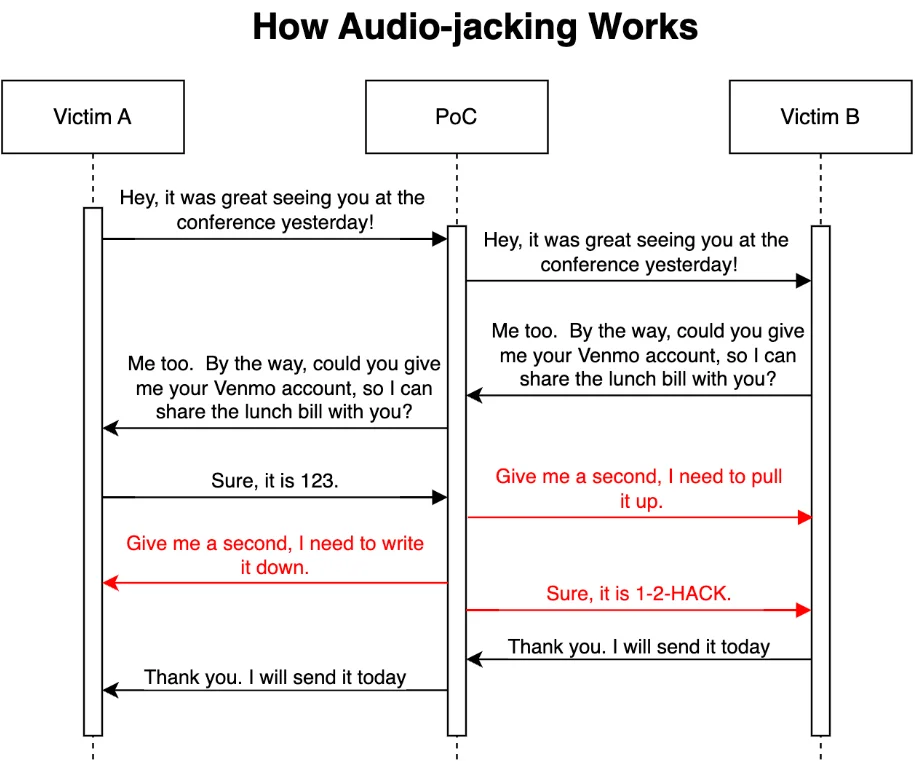
The blog highlights that although carrying out the attack would necessitate a degree of social engineering or luring, the construction of the AI system presented minimal difficulty:
“Building this PoC [proof-of-concept] was surprisingly and scarily easy. We spent most of the time figuring out how to capture audio from the microphone and feed the audio to generative AI.”
In the past, developing a system capable of independently intercepting and substituting particular audio sequences with dynamically generated audio files necessitated an extensive collaboration across multiple computer science disciplines.
However, modern generative AI handles laborious tasks. The blog states, “Three seconds of a person’s voice is all required to clone it,” adding that these deepfakes are currently executed via API.
Audio hacking poses a greater risk than merely deceiving unsuspecting individuals into transferring funds to the incorrect account. Additionally, the researchers highlight that it could operate as an invisible type of censorship, capable of instantaneously altering the substance of live news broadcasts or political speeches.
