Google introduced a series of improvements to its search engine on August 15, including advanced generative artificial intelligence (AI) features that, according to the company, will improve online information discovery and comprehension.

The most recent update extends the foundation of the company’s Search Generative Experience (SGE), which debuted in beta in 2023. SGE equips users with AI-driven contextual overviews and recommendations to improve search results.
The focus of generative AI is the creation of novel content from extant sources. From prior knowledge, prominent tools such as ChatGPT can generate text-based outputs such as poems and summaries.
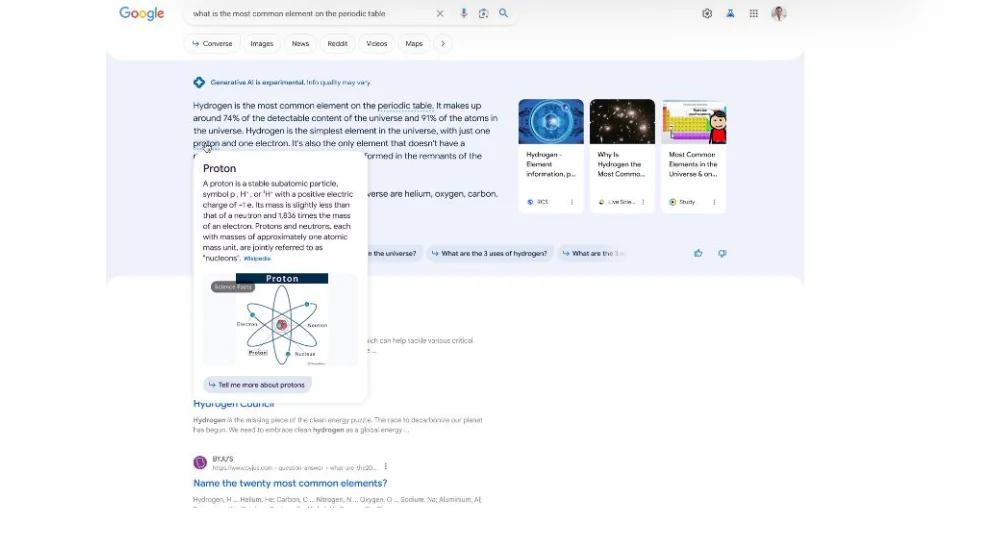
Currently, the introduced SGE feature is undergoing preliminary testing. After activation, users can tap an icon while browsing a webpage to access an AI-generated summary of the page’s primary topics. Each point is linked to its corresponding section, allowing easy navigation within extensive or complex articles.
Google’s artificial intelligence engine analyzes website content to identify key themes. According to Rany Ng, Google’s product lead, this procedure aids individuals in “enhancing comprehension and understanding of information,” whether attempting to comprehend complex ideas or locate specific details.
Microsoft’s Bing Chat has already implemented similar summarization capabilities, preceding Google’s February deployment of generative AI. Google asserts that its competitive advantage rests in comprehending web content and semantics.
Additional SGE enhancements focus on the comprehension of technical topics. AI-generated code summaries will emphasize syntax, facilitating understanding. Similarly, unfamiliar terms in AI-generated responses will disclose definitions and applicable diagrams when hovered over.
Google asserts that generative AI enhances search functions and facilitates the discovery of novel perspectives and insights. Nevertheless, a few experts warn that excessive reliance on AI could diminish an individual’s analytical skills.
Google’s privacy policy was updated on July 1, permitting it to use publicly accessible data for AI training.
