A new report from JP Morgan reveals that Ethereum’s Shanghai upgrade, which switched the network from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake, did not boost its performance as expected. The report analyzes the reasons behind Ethereum’s disappointing network activity and its challenges in the crypto market.

Ethereum, the world’s leading smart contract platform, underwent a major upgrade in April 2023 called Shanghai.
The upgrade was supposed to make the network faster, more scalable, and more eco-friendly by switching from a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a proof-of-stake (PoS) one.
However, a new research report released by JP Morgan on Thursday suggests that the upgrade did not have the desired impact on Ethereum’s performance and growth.
The Positive and Negative Outcomes of the Shanghai Upgrade
According to the report, the Shanghai upgrade positively affected Ethereum such as reducing its energy consumption by more than 99%, shrinking its supply, and increasing its staking activity.
The report estimates that about 14% of all ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of Ethereum, is currently staked on the network, accounting for 16 million tokens and a current value of over $26 billion.
Staking is a process where users lock up their funds on the network in exchange for rewards and security.
However, the report also found that the Shanghai upgrade did not translate into a significant increase in network activity, a key indicator of Ethereum’s adoption and utility.
The report noted that Ethereum’s daily transactions count has fallen by about 12%, daily active users have dropped by nearly 20%, and the total value locked in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications has decreased by almost 8% since the upgrade.
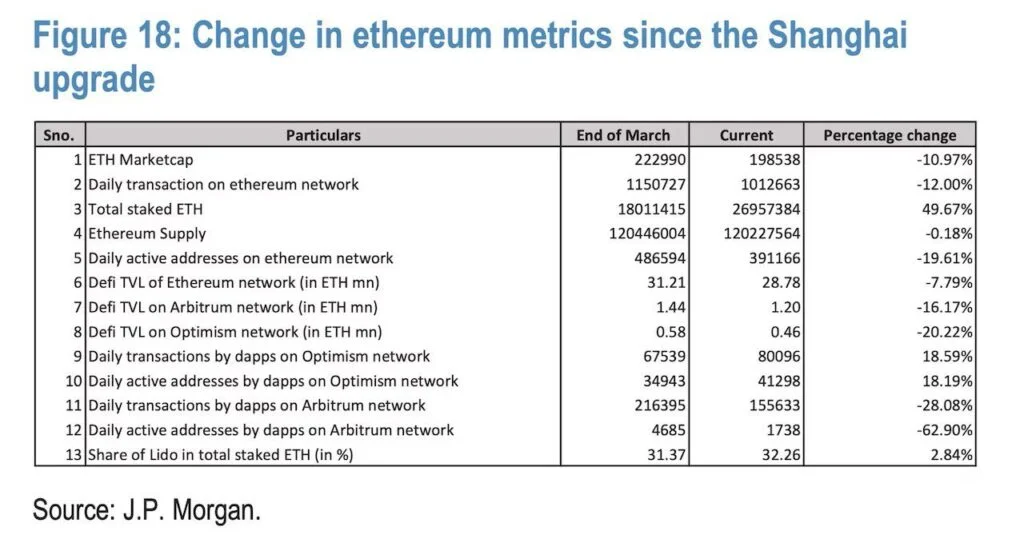
These numbers suggest that the upgrade did not boost Ethereum’s performance as anticipated.
The Possible Reasons for Ethereum’s Underperformance
The report offers several possible explanations for why Ethereum is not performing as well as expected after the Shanghai upgrade. Some of these include:
- The rise of competing blockchains that offer similar or better features than Ethereum, such as Solana, Binance Smart Chain, and Cardano. These blockchains have attracted users and developers with their lower fees, higher speeds, and innovative solutions.
- The regulatory uncertainty and crackdowns in some major markets, such as China and the U.S., have affected the crypto industry as a whole. The report cites the recent collapse of FTX and Terra, two prominent crypto platforms that faced legal troubles in their respective jurisdictions.
- The loss of interest and confidence from institutional and retail investors, who the volatility and risks of the crypto market have spooked. The report points out that Ethereum’s price has fallen by more than 40% from its all-time high of over $4,000 in May 2023.
- The technical challenges and delays that Ethereum faces in implementing its roadmap and vision. The report mentions that Ethereum still plans to introduce another upgrade later this year, called EIP-4844, which aims to improve its scalability and efficiency. However, the report warns that this upgrade may face potential setbacks and trade-offs.
What’s Next for Ethereum?
Despite its current challenges, Ethereum still remains the dominant smart contract platform in the crypto space, with a market capitalization of over $200 billion and a loyal community of users and developers.
The report acknowledges that Ethereum has a strong network effect and a rich ecosystem of applications and innovations that give it an edge over its rivals.
However, the report also cautions that Ethereum needs to overcome its hurdles and deliver on its promises if it wants to maintain its leadership position and achieve its long-term goals.
The report concludes that “the cryptocurrency market remains challenging at present” and that “Ethereum’s goal was to be greener and more efficient,” but it “didn’t grow as much as hoped after the upgrade.”
