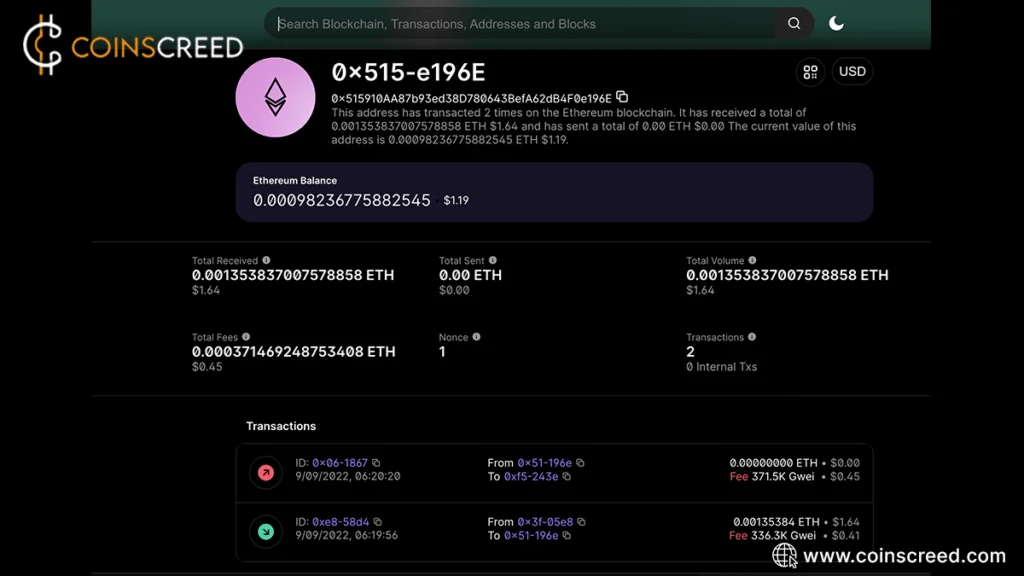
A block explorer is an online tool to view all transactions that have taken place on the blockchain, the current network hash rate and transaction growth, and the activity on blockchain addresses, among other useful information. You can think of it as a window into the blockchain world, allowing you to observe what’s happening on it.
What is a block explorer?
To provide some basic terms, a block explorer is a blockchain search engine that allows you to search for a particular piece of information on the blockchain. The activities carried out on crypto blockchains are known as transactions, which occur when cryptocurrencies are sent to and from wallet addresses.
Each transaction is recorded onto a digital ledger, known as a blockchain. Blocks on the blockchain are collections of transactions that were processed and approved by a group of third parties known as miners (for most Proof-of-Work cryptocurrencies).
In summary, a block explorer is an online tool to view all transactions that have taken place on the blockchain, the current network hash rate and transaction growth, and the activity on blockchain addresses, among other useful information. You can think of it as a window into the blockchain world, allowing you to observe what’s happening on it.
To assist users in using the block explorer, we have written this article for those interested in the concept of blockchain, its terminology, and its processes.
History Of Blockchain Explorer
The concept of blockchain explorers emerged simultaneously with blockchains.
This type of software emerged because it was difficult to interrogate blockchains,
Assume a friend tells you, “I sent you some cryptocurrencies.”
However, your wallet had not received any as stated.
This may be because the transaction was pending confirmation or had been rejected altogether. Or let’s say you sent crypto to a person and then they denied receiving any.
Second, it was hard to read the information in blockchains because it was set up in a certain way. While the information is stored and structured in a certain way, logically, it is indexed and grouped.
Some extra software was needed so that it could be read by the naked eye and by a regular user. Only experienced programmers were able to extract more information about transactions from blockchains. as meant for the Bitcoin blockchain, emerged in November 2010 at almost the same time when bitcoin was coming online.
The first explorer for Bitcoin was the equivalent of The explorer provided data about Bitcoin and, afterward, was moved to blockexplorer.com, where the real statistics page for the blockchain was posted. However, many of the real-time stats pages existed before Bitcoin block explorers.
In July 2010, the real-time stats pages get difficult, and a blockchain account was launched. Others, including decimal target, probability, hash rate next retarget, and superblock, came on after that. These tools were made because the old wiki’s block and difficulty values were hard-coded into the text, which made the information old.
What Is the Role of a Blockchain Explorer?
Blockchain explorers work by using a database that holds all blockchains in a searchable format and in tables. So, an explorer will use a node interface to first get all of the information from a blockchain. Once it derives the data, it then stores it in easily searchable tables.
It will gather the latest transactions and blocks and arrange them according to the defined searchable categories – for instance, wallet addresses transaction IDs, rich lists, balances, etc
An explorer also lets the user search for information by giving them a way to do so. In terms of technology, an explorer may use a relational database, a SQL database, and an API.
You may be already familiar with the fact that each blockchain comprises many distributed nodes. Each node that can directly read data on a blockchain grabs details of the latest transaction, mined block, and other data. This is then sent to the database, where the data is arranged into searchable tables.
This makes the Explorer fast to use. Most blockchains use 24 tables, including block, address, transaction, etc. Each row has a distinct ID or key, such as a unique identifier for blockchain addresses. Others create a unique key.
The user interface server for Explorer then creates a web page that allows it to interact with a user by way of the latter’s input of searchable terms. It also provides an API to interface with other computers. These are sent to the backend server in a server-readable format, and the backend server then responds to the user interface server for the search terms.
The user interface and API then send the web pages as HTML to the browser to allow the reading of responses by the user.
Why Use Blockchain Explorer?
Blockchain wallets can provide different kinds of data, but the view is limited to the data related to the keys that the wallet manages. Explorers are used to seeing information about all of the wallets in a blockchain’s transactions.
- Transparency: They allow you to check balances and smart contract addresses to see when users are participating in an initial coin offering (ICO.
- Checking if a wallet address is valid on the blockchain before sending crypto to a person.
- Checking if a transaction has been sent to the person it is being sent to. It is like having some public evidence that you have sent through cryptocurrencies to the person. Owners can check their wallet balances.
- Explorers can help to explain what is wrong with transactions that have not yet gone through or been confirmed and the stages of confirmation.
- It can help a user to know the current cost of a transaction or gas and therefore help to plan gas spending for future transactions.
- Sometimes it can help to know if a group is the one that mined a transaction and probably help in making decisions of whether to invest more computing resources for future mining activity.
- It can help user developers who are programming their wallets if they are working properly to send and receive and store cryptocurrencies.
- Explorers can be used alongside other software such as nodes to corroborate data and information, for instance, to confirm other tools whether are working appropriately.
- Developers can also check what functions and features they need to include in their wallets or other software using these explorers.
- As research tools, explorers can help make important decisions related to personal, group, and company finances.
Conclusion
Blockchain explorers are used to looking at the details of a particular block on the blockchain. They also show basic information about transactions and addresses.
These details may include the block height, the timestamp when it was mined, and the list of transactions within the block. Thus, tracking the progress of the blockchain and ensuring that new blocks are added to the chain on time has become easier than ever before.
Also, some other block explorers have more advanced features, like the ability to look at the code of a smart contract and change it. This benefits the developer who are building applications on top of a specific blockchain.
