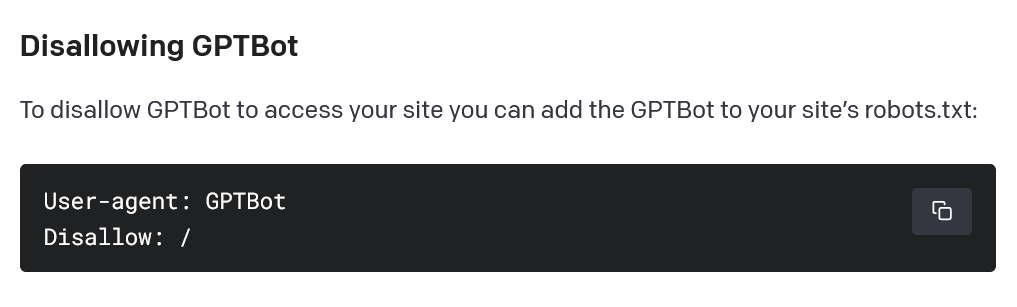
ChatGPT users have the option of disabling the web crawler by including a “disallow” command in a standard server file.

According to the company, OpenAI’s “GPTBot” is a new web crawling tool that could conceivably enhance future ChatGPT models. “Web pages crawled with the GPTBot user agent may potentially be used to improve future models,” OpenAI wrote in a new blog post, adding that it could increase accuracy and expand the capabilities of future iterations.
A web crawler, also known as a web spider, is a form of bot that indexes the content of websites on the web. They are utilized by search engines like Google and Bing for websites to appear in search results.
OpenAI stated that the web crawler will collect publicly accessible data from the internet, but exclude sources that require paywalls, are known to collect personally identifiable information, or contain text that violates its policies.
Breaking 🚨
OpenAI just launched GPTBot, a web crawler designed to automatically scrape data from the entire internet.
This data will be used to train future AI models like GPT-4 and GPT-5!
GPTBot ensures that sources violating privacy and those behind paywalls are excluded. pic.twitter.com/oR3kY4buaU
— Shubham Saboo (@Saboo_Shubham_) August 7, 2023Website proprietors can block web crawlers by adding a “disallow” command to a standard server file. Three weeks before the release of the new crawler, the company filed a trademark registration for “GPT-5,” the successor to the current GPT-4 model.
The application, submitted to the United States Patent and Trademark Office on July 18, concerns the term “GPT-5,” which includes software for AI-based human speech and text, audio-to-text conversion, and voice and speech recognition.
However, observers may refrain from holding their breath for the next version of ChatGPT. Sam Altman, the founder, and CEO of OpenAI, stated in June that the company is “nowhere close” to beginning GPT-5 training, citing the need for multiple safety audits before starting.
Concerns about OpenAI’s data-gathering methods have recently been expressed, particularly regarding copyright and consent. Japan’s privacy commission issued a warning to OpenAI in June regarding collecting sensitive data without permission, while Italy temporarily banned ChatGPT in April because it violated multiple European Union privacy laws.
In June, 16 plaintiffs filed a class action lawsuit against OpenAI, alleging that the AI company accessed private information from ChatGPT user interactions. If these allegations are confirmed to be accurate, OpenAI and Microsoft, also named as a defendant, will violate the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, a statute with a precedent for web-scraping cases.
